Panicled hydrangeas are among the most popular summer shrubs. They do not require much effort from the gardener in order to delight him with flowering throughout the summer. One of these varieties is Summer Snow. This is a small, compact shrub that begins to bloom in July and continues until September. Read about how to plant and grow Summer Snow in a summer cottage.
Botanical Description
Panicled Hydrangea Summer Snow (Hydrangea paniculata Summer Snow) - a small shrub up to 1 m high and a diameter of about 0.9 m. It has upright strong shoots strewn with green egg-shaped leaves. At the ends of the shoots, cone-shaped inflorescences, called panicles, are formed. They consist of sterile cream-white flowers. Panicles reach a height of 25 cm.

The variety was obtained in Poland in 2018 by Alex Frederick Shoemaker (Schoemaker). Recommended for planting in flower arrangements, but can also be grown in containers. Summer Snow bouquets are great for cutting. Involved in landscape design as an accent plant and decoration of garden paths. Landed next to clematis, host, phlox.
Important! During flowering, hydrangea branches grow heavier and tend to the very ground. Therefore, be sure to provide a garter of flowering shoots.
Variety Characteristics
Distinctive features of the variety are that its flowers fade very elegantly, gradually turning yellow. In combination with red stalks, they remain decorative even when dry. On the old shoots, the bark peels off and through it you can see wood of golden color, which also gives the bushes additional decorativeness.

Detailed characteristics of the variety:
| A type | bush |
| Height | 1m |
| Width | 0.9 m |
| Growth rate | average |
| Lives until | 40 years |
| The soil | well-drained, nutrient rich |
| Watering | moderate regular |
| Lighting | sun or partial shadow |
| Bloom | summer |
| Colour | creamy white but may later change to pinkish white |
| Diameter of inflorescences | 5 cm |
| Leaves | green with lighter veins |
| Winter hardiness | 7 USDA (-17 ° C) |
| Tolerance to urban pollution | high |
 The bush has no significant negative properties. But since it is not too frost-resistant, gardeners recommend covering the trunk area with a thick layer of mulch to protect the roots from frost.
The bush has no significant negative properties. But since it is not too frost-resistant, gardeners recommend covering the trunk area with a thick layer of mulch to protect the roots from frost.
Landing
Panicled hydrangea bushes grow well in partial shade and in sunny areas. But it will be preferable to plot in which the sun shines brightly before dinner, and in the afternoon the shadow from the trees falls. When planting in an area with bright sunlight throughout the day during the hottest hours, it is recommended that plants be shaded.
Important! When planting hydrangeas, you can not use ash or lime, since they make the soil neutral or alkaline, while the bush needs acidic.
Site selection and preparation
The soil must be rich in nutrients. The most suitable are sandy soils. They hold mineral substances well, easily warm up and allow air to pass through, and slowly dry. If the soil is sandy, then it is supplemented with compost, humus, peat or other organic matter. The application rate is 2 buckets per 1 sq. Km. m

Clay soil is also ennobled. It is too dense and organics in it is only 5%. Therefore, sand is added for looseness, and humus is added for nutrition. Black soil is considered the most fertile soil. They have a lot of organics, they perfectly pass air. But after a few years of growing plants, their nutritional value falls. Plants use nutrients while leaching and oxidizing the soil.
 Such a site is suitable for hydrangeas - the required level of acidity is 4.5–5 pH. She prefers a slightly acidic environment.
Such a site is suitable for hydrangeas - the required level of acidity is 4.5–5 pH. She prefers a slightly acidic environment.
If organic fertilizers are applied during planting, they will maintain the desired soil acidity. Plants are planted in spring or autumn. Air temperature at this time should not be lower than + 10 ° С. At moderate temperatures, rooting is more effective. Autumn planting can be recommended only in those regions where the winter temperature does not fall below -10 ° C.
Did you know? In Japan, hydrangea is considered a talisman from dark forces and a flower that brings incredible luck.
Seedlings preparation
Remove the seedling from the container. Inspect the root system. Roots are recommended to be slightly shortened - by 2 cm. This is necessary to stimulate the growth of the root system. Existing shoots can also be shortened to 3-4 kidneys. Thanks to this operation, you save the strength of the plant and direct them to growing roots. The result is a more powerful and viable bush.
 You can also soak the roots in a solution of "Kornevin" or other growth stimulant for the time recommended in the instructions.
You can also soak the roots in a solution of "Kornevin" or other growth stimulant for the time recommended in the instructions.
Landing rules
For planting you will need: a shovel, a garden hoe; humus or compost 1-2 buckets for each bush; sand, pebbles or rubble.
Landing Instructions:
- A pit with a size of 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 m is prepared. Ideally, it should be 2-3 times the diameter of the root ball.
- A layer of drainage is laid at the bottom. It can be pebbles, small stones, gravel. Layer thickness - 20 cm.
- The soil removed from the pit is diluted with compost and sand if necessary. You can add needles instead of sand. It not only loosens the soil well, but also serves as an additional long-lasting fertilizer.
- A part of the prepared substrate is laid on the drainage layer.
- A seedling is placed on top.
- Fill up the earth. In the process, you need to control that the root neck remains at the same level at which hydrangea grew in the container.
- Watered with 1-2 buckets of water.
- Seal the soil and fill the earth.
- A layer of mulch is laid on top. Thickness - 5–7 cm. It can consist of needles, peat, sawdust, bark. Mulch protects the soil from compaction, prevents the growth of weeds and excessive evaporation of moisture.

Care
In the future, hydrangeas need to be provided with watering, regular fertilizing and periodic prevention of diseases and pests. Also, the bushes are periodically pruned to rejuvenate and carry out general garden care measures: in the autumn they remove the leaves and prepare the plants for wintering, in the spring they remove the broken or dried branches, in the summer after flowering they remove the faded inflorescences.
Watering
The Latin name of the plant is Hydrangea, i.e. vessel with water. And this very accurately conveys the needs of the bush in moisture. During the first year after planting, 2 buckets of water are placed weekly under each bush. You can water 1 or 2 times a week, as the soil dries. An adult plant is watered weekly. But if it rains, then 1 watering in 2 weeks is enough.
Top dressing
They feed plants with organic fertilizers or store, mineral. Each group has its own merits. So, minerals consist of one or more components. For example, ammonium nitrate is a source of nitrogen. It has 40% of it. And potassium sulfate is a source of potassium compounds.

The complex mixtures, for example, Kristalon, Aqua, Agricola, will contain nitrogen, potassium and phosphorusnecessary for the development of plants. Mineral mixtures are quickly released and enter the plant almost immediately. And organic ones are released more slowly, but they can nourish the bush for a long time. In addition, peat, compost and other substrates contain much more compounds than the 3 above and will be more useful.
Important! Hydrangea is partially toxic. Therefore, its leaves and flowers are not eaten to avoid indigestion.
Plan for a minimum of 2 top dressings for the bush:
- The first - In early spring before budding. It can contain 15 g of potassium sulfate and superphosphate, as well as 10 g of urea. They are bred in 10 liters of water and watered bush.
- As soon as the buds appear, plan 2 feeding. It will contain 20 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate. Urea is no longer needed. It is a source of nitrogen, necessary only at the beginning of the growing season.
Haircut and Shaping
Trimming refers to a set of measures, including:
- sanitary pruning;
- molding;
- rejuvenation.
Sanitary pruning is the removal of dried or damaged branches. It is planned for the end of February or any time from November to March - while the plant is at rest. Spend it annually.
 Hydrangea branches eventually lose their ability to flourish. Therefore, once every 3-5 years old shoots are removed. Cut them to the ground. This stimulates spring growth of new ones. By terms, rejuvenation is combined with a sanitary haircut.
Hydrangea branches eventually lose their ability to flourish. Therefore, once every 3-5 years old shoots are removed. Cut them to the ground. This stimulates spring growth of new ones. By terms, rejuvenation is combined with a sanitary haircut.
As for molding, an ordinary bush does not need it. But if you grow a standard plant in a tree form, then you need to regularly remove the "extra" shoots. Note that the size of the inflorescences is associated with pruning. The more branches you removed, the more magnificent the inflorescences will turn out. But you can’t cut too intensively so as not to harm the hydrangeas, because when removing more than 1/3 of the green mass, the bushes get sick and can die.
 1 - planted young plant with buds; 2 - spring shortening of the shoot; 3 - bending continuation shoot; 4 - pinch of shoots of the current year; 5 - removal of last year's shoots for the formation of the stem; 6 - removal of shoots formed on the stem; 7 - formation of the crown from the shoots of last year; 8 - shtamb with a height of 0.5 - 1 m.
1 - planted young plant with buds; 2 - spring shortening of the shoot; 3 - bending continuation shoot; 4 - pinch of shoots of the current year; 5 - removal of last year's shoots for the formation of the stem; 6 - removal of shoots formed on the stem; 7 - formation of the crown from the shoots of last year; 8 - shtamb with a height of 0.5 - 1 m.
Wintering
Summer Snow is intended for cultivation in areas with a minimum winter temperature of -17 ° C. This means that where the frost is stronger, the flowering buds will be damaged by the cold and the bush will not bloom at all.
In those regions where the air temperature meets the requirements, the foot of the bush must be covered with mulch. The layer thickness is 7-10 cm. Do this after the temperature drops to 0 ° C. The mulching layer will act as an insulator, preventing sudden changes in soil temperature, as well as freezing of the root system.
In order to protect the buds from frost, some gardeners install a net around the bush and fill it with foliage. It is used for this foliage of chestnut and other infertile trees. It is believed that fruit foliage quickly accumulates moisture and promotes decay.

Breeding methods
All flowering plants, without exception, can propagate by seed. But in hydrangeas they are formed too little. Therefore, gardeners propagate bushes by cuttings, layering. Both methods are equally convenient to use and easy to implement.
Seeds
Seed propagation is one of the most difficult. First of all, because hydrangeas have very little seed material - almost all flowers in the inflorescence are sterile. And those that turn out have low germination - about 50%.
Did you know? In Victorian England, it was believed that hydrangeas symbolize boasting. After all, their very magnificent flowering gives very few seeds.
But if there are seeds and desire, then this is done as follows:
- A container is prepared for planting. A mixture of compost, peat and sand is poured into it.
- The substrate is treated by irrigation with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.
- Seeds can be soaked in water or a growth promoter to improve germination.
- Then they are sown, pressed lightly to the ground and sprinkled with sand on the surface.
- Cover the container with film to create a greenhouse effect.
- Installed in a well-lit room, but not in direct sunlight.
- Until germination, soil moisture is maintained under the film. After germination, it is removed.
- Within 2-3 years, the seedlings will grow in the container, gradually adding to the growth. They can be planted in the soil when they reach a height of 30–40 cm.
 When propagating by seeds, it is important to consider that most varieties are hybrids. They do not necessarily copy the basic features of the mother plant. To obtain an exact copy, you need to use other methods of reproduction.
When propagating by seeds, it is important to consider that most varieties are hybrids. They do not necessarily copy the basic features of the mother plant. To obtain an exact copy, you need to use other methods of reproduction.
Layering
By propagation by layering is meant the pressing of one of the shoots to the ground. It is fixed with a metal bracket. Sprinkle with soil on top. Watering, keeping the earthen hill moist. Each internode that is sprinkled with soil can take root.
Then, growth points appear on the rhizome, and you can get several new plants from one layer. Next year, transplant the resulting new plants to a permanent place, separating them from the mother plant.
Vaccinated
Vaccination is a combination of several plants. Wherein as a rootstock, a variety with higher frost resistance or disease resistance is used, and as a graft, a weaker but decorative. In this way, a tree-like form of hydrangea is obtained. As a stock, a lilac is used, because it has a characteristic straight trunk, and a twig of panicled or tree-like hydrangea is planted on it.
Cuttings
Cuttings are the most used method of propagation of shrubs. To do this, cut a young, healthy branch at the end of June. The bark on it will be fresh and greenish, unlike the old branches covered with gray bark.
Did you know? The cut branches of hydrangea cannot stand in a vase for long. To prevent rapid wilting, their ends are immediately immersed in water, then removed and slightly dried for 10 minutes, and then lowered into a container with boiled water for 30 seconds, after which they are placed in a vase.
Reproduction Instructions:
- The branch is divided into several parts. Each of them must have at least a pair of internodes. The approximate size of the handle is 15 cm.
- Leaves are removed from the lower internodes. Leave only the top pair. If they are too large, then cut the sheet plate in half.
- Dip the lower end of the stem into a root growth stimulator. It can be "Kornevin", "Heteroauxin" or "Zircon". Observe the concentration of the solution and the exposure time in accordance with the instructions on the package for the drug.
- A mixture of peat and sand is placed in a new container. If a used pot is taken for propagation, then it is necessarily washed well with soap and the substrate is disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate 1%.
- The prepared soil mixture is moistened. They make holes and plant cuttings there.
- Seedlings are covered with polyethylene. But they do it so that the film does not lie on the plants, but rests on some kind of props. For example, wooden sticks.
- The pot is installed in a bright room with a temperature of + 20 ° C.
- Periodically check the condition of the soil and then, it is somewhat moist. Watered.
After a couple of weeks, when the plants take root, remove the film and grow them indoors. But you need to remember that hydrangea is a deciduous shrub. She needs a period of winter cool. Therefore, in autumn, seedlings can be put on a glazed, but unheated balcony. The air temperature there should not fall below -5 ° C.
Dividing the bush
Usually they divide old bushes that are overgrown. They plan an event in the spring - April or the end of March, if it has already snowed. For this, the bush is dug up and removed from the soil. Inspect it carefully. Part of the shoots along with part of the root system must be separated, causing a minimum of damage.
The received parts should be planted in a new place in prepared wells. The distance between the planting pits is at least 70 cm. When planting near buildings, at least 50 cm is left between the wall and hydrangea.
Video: dividing an adult hydrangea bush
Diseases and Pests
Hydrangeas are rarely sick plants. But if the bush is planted in the wrong place - with a lack of sun, an excess of water, poor air circulation, then it will be sick more often.
The main problems of hydrangeas:
- Excess sunlight causes leaf burn. They discolor, turn yellow, fade.For such bushes, you need to organize shading in the afternoon.

- If there is not enough iron in the soil, then the leaves also discolor and turn yellow, but they still have green streaks. it chlorosis. It is treated by applying fertilizers containing iron and magnesium.

- Excess water causes putrefactive processes. The roots darken, become soft and die off. And the plant itself begins to wither. White cotton coating on the leaves - white rot. Use “Fundazole” or “Fitosporin” spray for treatment. Wet spots of gray color - gray rot. Later they become red-brown and the leaves fall off. Remove the damaged parts of the plant and spray with “Skor” or “Fundazol”.

- Powdery mildew - fungal disease. Her symptom is a dirty white coating on the leaves, similar to flour. The disease does not lead to the death of the plant, but causes leaf decay. It spreads through controversy, usually when the days are warm and the nights are cool. It is treated by removing the affected parts of hydrangea and spraying with copper-based preparations. For example, Bordeaux liquid 1%.
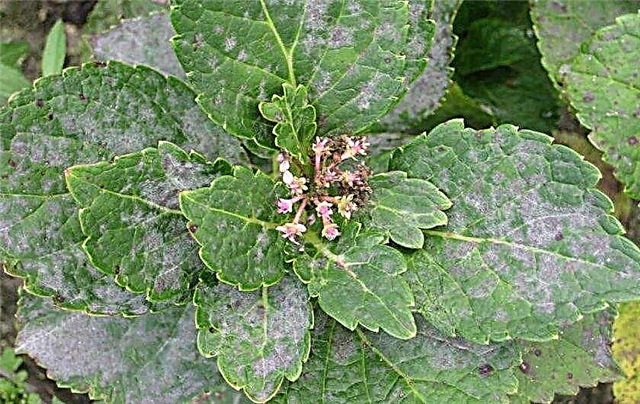

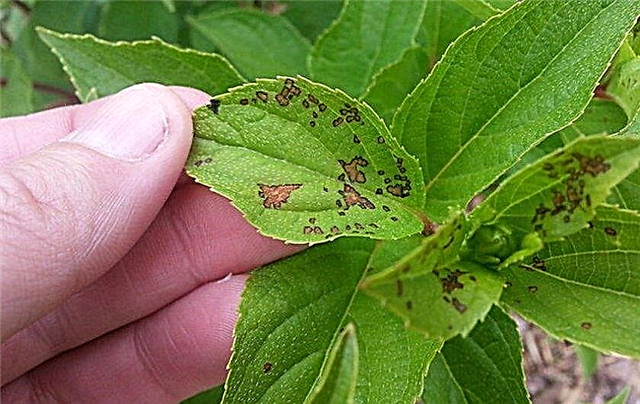
- Leaf spotting - also a fungal disease. Brown spots appear on them, which gradually increase in size. For the treatment, bushes are treated with copper chloride at the rate of 40 g of the product per 10 l of water.

- Rust - a fungal disease that manifests itself as rounded spots on the leaves, the tops of which become brown or yellow and eventually fall off. Spores of rust spread in water or in the wind, so do not spray the bushes with moisture from above. Use bordeaux liquid 1% for processing.

Hydrangea bushes can be attacked by pests. Most of these insects are polyphagous, that is, they affect not only hydrangeas, but also other garden crops.
Did you know? The birthplace of hydrangea are considered the mountain islands of Japan. There is still a maximum species diversity.
The main pests:
- Most common in summer - aphids. Among them - hawthorn, beetroot, green peach. These are small insects up to 0.7 mm long with an oval body of green or dark color. They settle in colonies on young leaves and tops of shoots. Destroy them by spraying plants with a soap solution (15 g / 1 l of water).

- Ticks also frequent guests in the garden. These are small, up to 0.3 mm insects that settle on the underside of leaves and in cracks in the bark. Among them: a fruit red tick, Turkestan spider web, ordinary spider web and others. Signs of their appearance will be a lot of small discolored spots on the leaves in places where they were bitten by insects. To control pests, Actelik is used.

- Black cherry weevil - This is an oblong beetle with a long nose-trunk. It damages the leaves, which makes them brown and holes form in them. But unlike a tick, holes from a weevil are not covered by cobwebs. To combat the pest, spraying with Fufanon-Nova is used before flowering the bushes.

- Japanese beetle (shield bug) - a large insect with bronze-green wings up to 6 mm wide and up to 12 mm long. They can be found on the bushes in the morning. Leaky leaves will be a sign of the presence of these beetles on hydrangeas. The easiest way to shake them off the branches in a bucket of soapy water. If there are too many beetles, the treatment of bushes with Metabrom-RFO (gas) is used.

It’s easy to grow hydrangeas. They grow well in any gardens and can acclimatize everywhere in a temperate climate. Following the simple rules for caring for plants, you will admire the lush flowering bushes throughout the summer.