Violet Panacota will appeal to those who prefer to grow Saintpaulias of light color with large and double flowers. Such a plant will become a decoration of a home greenhouse, the main thing is to properly organize the growing conditions and ensure proper care. This will be discussed further.
Botanical description of the plant
AV-Panakota is a hybrid cultivar of violets, the result of the work of the breeder from Moscow A.P. Tarasov, who introduced the flower to the world in 2013. For 5 years, his flowering creation managed to win the recognition of florists from different countries.
Did you know? In Italy, Panacotta is called a very gentle, light and airy dessert made from cream and gelatin. Literally, this term translates as “boiled cream”.
Among the characteristic features of the variety are the following:
- large (up to 7–8 cm in diameter) flowers with wavy edges and a predominantly white color (a light pink color can be seen only in the center of the petals, and bright green ruffles on the lower petals);
- the leaves of the plant are dark green, slightly wavy along the edges and elongated in length;
- leaf rosette - medium size, slightly elevated above the surface of the soil.
The conditions for growing violets at home
For Panacota violets, it is important to properly place in the house, with the organization of sufficient lighting, maintaining the required temperature level and suitable humidity indicators.
Placement and lighting
A good place to place flower pots is the windowsills of the southeast and east windows, providing a stream of light for 10-14 hours every day. True, at lunchtime, you have to shade the windows, protecting the violet leaves from increased solar activity, which can leave them unattractive burns.
Important! If the room temperature drops sharply, and the violet drops, try to return it to heat as soon as possible. By timely removing damaged tissue and preventing the spread of rot, you can still save the flower.
For the same reason, it is not recommended to put pots on the southern window sills, where exposure to the sun most of the time can not be called gentle. If you want to extend the flowering of violets for the winter period, you will have to arrange artificial lighting with fluorescent lamps, lighting up plants in those periods when there is not so much natural sunlight as in summer.
Temperature and humidity
Like many other senpolias, Panakota prefers a warm climate, therefore, in the place of its growth, the temperature values should not fall below + 20 ° C, and for young plants it is desirable to increase them to + 25 ° C. The optimum air humidity will vary between 50-60%. Lowering the temperature negatively affects the appearance of the flower and, first of all, it is noticeable by wilted foliage and showered peduncles.
Courts Rules
Caring for violets provides for the organization of timely watering, compliance with the feeding regimen, partial or complete crop pruning, and transplanting as they grow. Consider each of these processes in more detail.
Watering technique
Watering Panakota violets is carried out as necessary, that is, with the obligatory taking into account the state of the upper soil layer in the pot. As soon as it condenses and dries 2 cm deep, it’s time to take on the watering can. Water for irrigation should be settled, room temperature (not lower than + 16 ° C) and free of chlorine or heavy metals.
Did you know? In addition to decorating the house, violets “clean” the air in it. These plants secrete volatile phytoncides, which have a beneficial effect on the psychological state of a person, normalize their heart rate and increase efficiency.
As for the irrigation method used, it is better that it be radical, with a clear direction of the thin stream under the stem of the violet. The leaves and flowers of the plant should be protected from possible moisture, which will retain their external attractiveness for a long time. On average, in the summer, soil moistening in a pot with a violet is performed after 1-2 days, and with the advent of cold weather it is reduced to once a week.
Top dressing
Violets need nutrition during a period of intensive growth and the formation of flower brushes, and complex mineral fertilizers with a high content of potassium, phosphorus and other useful micro- and macrocells are suitable for the role of nutrients. Sometimes organic compounds are also used to accelerate flower growth: a solution of manure or humus mixed with water in a ratio of 1:15. However, you need to be extremely careful with them, because a high nitrogen content in the soil can damage flowering. During the growing season, the frequency of fertilizer application should be 1 time in 2-3 weeks, and top dressing should be combined with watering. In its pure form, both mineral and organic substances can burn the delicate roots of a flower.
However, you need to be extremely careful with them, because a high nitrogen content in the soil can damage flowering. During the growing season, the frequency of fertilizer application should be 1 time in 2-3 weeks, and top dressing should be combined with watering. In its pure form, both mineral and organic substances can burn the delicate roots of a flower.
Important! Uniflor, Mr. Color, Etisso, and Pokon are considered to be proven complex fertilizers to stimulate the flowering of violets today, the dosage and rules of use of which are always indicated on the package.
Pruning
Pruning Panakota violets is carried out only with the aim of ridding the plant of wilted, dried and damaged parts. In addition, to increase the decorative properties, flower growers often remove the lower leaves, especially if they touch the surface of the soil and can cause the development of putrefactive processes.
You can cut off the excess parts only with a well-disinfected knife and, mainly, in the spring, when the flower leaves the state of winter dormancy. Treat the cut points with charcoal or activated carbon, which will prevent rotting of the crop.
Transfer
Violets are transplanted due to their increased size mainly in the spring, but changing the pot due to the development of putrefactive processes or any other good reason can be done at any time of the year. On average, Panacot's senpolia is transplanted with a regularity of once every 1-2 years, when the former pot becomes small, and the nutrient deficiency in the soil is already noticeable: the color of the flowers dims, they fade, and the leaves of the plant wilt.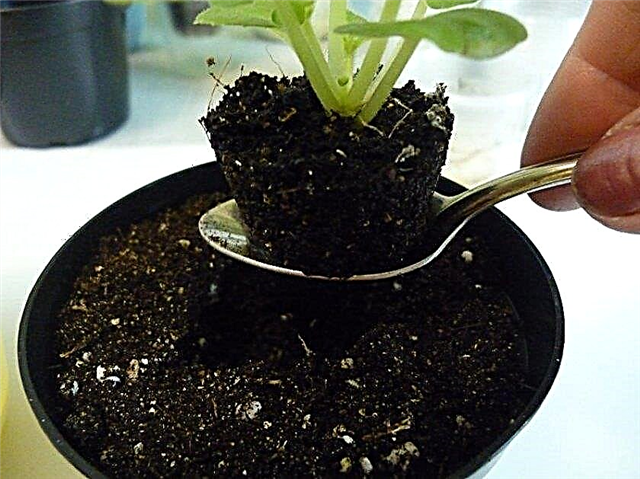 The new landing capacity should be 2-3 cm larger than the previous one, which will provide the plant with comfortable conditions for growth. As a new substrate, you can use ready-made soil for flowering plants (sold in flower shops), or you can prepare it yourself by mixing, for example, 3 parts of peat soil, 1 part of leaf soil, one part of vermiculite and perlite, as well as ½ of charcoal . Before planting, it is useful to shed soil in pots with fungicidal preparations (for example, Fitosporin), thereby disinfecting it and destroying pathogens.
The new landing capacity should be 2-3 cm larger than the previous one, which will provide the plant with comfortable conditions for growth. As a new substrate, you can use ready-made soil for flowering plants (sold in flower shops), or you can prepare it yourself by mixing, for example, 3 parts of peat soil, 1 part of leaf soil, one part of vermiculite and perlite, as well as ½ of charcoal . Before planting, it is useful to shed soil in pots with fungicidal preparations (for example, Fitosporin), thereby disinfecting it and destroying pathogens.
Important! Leave at least 1 cm of free space between the edge of the pot and the ground, which will facilitate the irrigation process and prevent the leakage of fluid from the outside of the pot. With excessive subsidence of the soil, it can always be supplemented with the remaining substrate.
The process of transplanting violets Panakota is simple and consists of:
- Preparing the pot with the drainage and soil layers covered in it (the level of the latter should correspond to the middle of the tank).
- Extracting a flower from an old pot (in order to facilitate the task and not damage the violet rhizome, it is worth watering the plant in advance with plenty of warm water).
- Placing the culture in a new tank and filling the remaining space with the prepared soil mixture.
Video: violet transplant
How to propagate at home?
More often, Panakota violet is propagated by a cut leaf, that is, a cuttings, but in some cases, when the plant grows very much, it can be propagated by dividing the bush or detaching the children. Consider each of the options.
Cuttings
Cutting violets involves a neat cut from the mother plant of a healthy medium-sized leaf and its rooting in water or soil, with further planting in a separate pot. It is advisable to look for a suitable stalk in the middle of a leaf outlet, choosing only a clean and even slightly shiny specimen, without the slightest sign of damage by diseases or pests.
After cutting with a sharp knife (the place of cutting is powdered with crushed charcoal), it is immersed in water and put in a shaded place for root formation. It is desirable that the container for rooting the cuttings was made of dark glass, and inside it was chilled boiled water with an activated carbon tablet dissolved in it.
The stem of the leaf is immersed in the liquid no more than 1 cm, and if after a few days it becomes smaller - you can always add more clean water. It will be possible to transplant the stalk into the soil when the roots that have appeared from the cut grow to 1 cm in length.
If you are afraid that the cut leaf will begin to rot in the water and you will lose the harvested planting material, you can try to root part of the violet directly in the soil, poured into disposable glasses, with holes in the bottom. It is necessary to place the handle in such a container at an angle of 30–45 °, for which purpose the tilled soil is lightly compacted and the leaf plate is propped up with a toothpick.
To speed up the process of germination, it is important to cover the glasses with a plastic bag, thereby achieving a greenhouse effect. A grown violet is transplanted to a constant place of growth only when its new leaves reach a diameter of more than 3 cm.
Video: propagation of violets by cuttings
Dividing the bush
When it grows, the violet Panakota forms the beginnings of new bushes, and in some cases young outlets even interfere with the main bush, occupying the space intended for it. In such situations, plant propagation by dividing the bush is not only justified, but also necessary, as it ensures the further development of the maternal form.
The process of propagation of a flower in this way consists of:
- Carefully extract the socket of the mother plant from the pot.
- Branch of a young outlet (you can carefully break it off at the junction with the mother bush) and remove the bottom long leaves.
- Transplantation of the seized planting material into a new substrate or container with water, if the root system on the outlets is poorly developed.
Video: propagation of violets by dividing the bush
Growing difficulties
Difficulties in growing violets are almost always associated with diseases and pests. On the violet Panakota, insects such as aphids, springtails, whiteflies and scaleflies, each of which depletes the plant's nutritional reserves and leads to limited growth and shredding of flowers. Characteristic for this cultivar senpolia disease: gray rot, powdery mildew and leaf spot, significantly spoiling the appearance of the plant.
The most effective ways to eliminate these problems are the use of fungicides and insecticides, among which the most effective are Actellik, Aktara, Fitoverm, Iskra (help cope with harmful insects), as well as Previkur, Topaz, "Fundazol", "Fitosporin-M", which are used in the fight against fungal ailments and rot.
Subject to the standard rules for the cultivation of violets, serious problems with the cultivation of Panakota should not arise, because it does not differ in increased demands on planting and further care. The reward for the efforts will be a gentle and light Saintpaulia, pleasing to the eye all year round.