Human life is impossible without vegetables, because they are rich in fiber, and also contain a large number of nutrients that the body needs for normal functioning. Growing sweet peppers, you should pay attention to the variety Fat Man, superior in quality to many modern hybrids.
Description and characteristics of the variety
Originally a vegetable from America, it is known for about 9 thousand years and has up to 2 thousand varieties. The fat man was bred by cross-pollination of different varieties, so this variety gives offspring with realized genetic potential only in the first generation. This means that collecting seeds does not make sense, since the fruits will yield to the parental form, and may not germinate at all. Fat man is referred to as thick-walled representatives of the species, due to which the vegetable is very juicy and sweet. They grow crops in regions with a warm climate; for seed germination, a temperature of at least +26 ... + 28 ° C is necessary.
Productivity
The variety is classified as mid-season high-yielding type. Fruits can be harvested on the 115th day after planting. The yield index reaches up to 4.5 kg per 1 m². To obtain this result, it is important to comply with all the requirements of agricultural technology.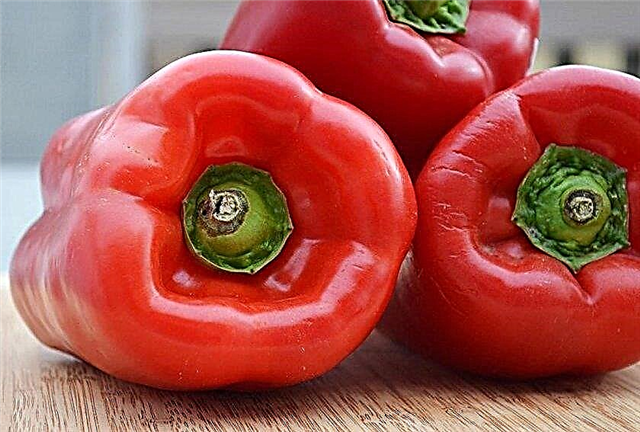
Description of the bushes
The bushes are tall, semi-sprawling, grow to a mark of 50 cm. The foliage is medium-sized, wrinkled, has a rich green color.
Description of the fetus
The vegetable is large: grows in length up to 12 cm, and in diameter - up to 8 cm, wall thickness - 5-10 mm. One fruit weighs about 150 g on average. It resembles a prism in shape; ribbing is weakly expressed. The pepper is saturated red in color with a smooth surface, the peel is dense, which allows the fruit to be transported without any damage to the shell. The variety is endowed with high taste, its walls are fleshy, juicy, sweet without impurities bitterness.
Did you know? Sweet pepper fruits are considered a natural antidepressant due to the high content of B vitamins.
Pros and cons of the variety
When growing Fat, it is important to consider all the positive and negative sides of the variety.
- The advantages can be considered:
- high productivity;
- disease resistance;
- immunity to environmental conditions (temperature jumps, high humidity, etc.).
- The disadvantages include:
- first generation sterility;
- expensive planting material.
Features of growing varieties
In order for the crop to be rich, you need to follow a number of simple rules, which are listed below.
Dates and seed preparation
Depending on where the pepper will grow, determine the timing of its planting. So, for cultivation on open ground, sowing is carried out in late March, for greenhouse vegetables - in mid-February. Before sowing, the seeds are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, soaking them for 20 minutes, and then dried.
Important! Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out for 2–2.5 months before disembarkation.
Preparing land for seedlings
For good germination rates of seedlings, sowing grains in ordinary soil is not enough.
For this purpose, you should prepare a special mixture or buy a ready-made one consisting of:
- Humus. Enriches the substrate with nutrients.
- Peat. Makes the soil more loose and ensures its saturation with moisture.
- River sand. Gives soil porosity.
- 1 part of turf land;
- 1 part peat;
- 1 part of sand.
- 30 g of superphosphate;
- 30 g of sulfate;
- 10 g of urea.

Sowing seeds
The culture does not tolerate picking, for germinating seedlings it is recommended to give preference to individual peat pots. A small diameter is up to 10 cm, the rhizome develops rather slowly, so it makes no sense to use large dishes.
A special substrate is also prepared by mixing:- 2 parts of humus;
- 1 part of the earth;
- 1 part of sand.

Seedling Care
Having planted seeds, water the soil. Pots are placed in a room with a temperature of + 22 ° C. Lighting is completely unimportant; it can also be placed in the dark. After the seeds germinate, the temperature is kept during the day from +26 to + 28 ° С, at night - from +10 to + 15 ° С. Watered sparingly, avoiding drying out of the earth's coma, for this use warm water with a temperature of up to + 30 ° C, otherwise the plant will be weak.
It is also important to avoid drafts, but do not forget about airing the room. Regular spraying will beneficially affect the growth of seedlings. Emerging shoots require additional lighting from 7 am to 9 pm. Before planting, young plants must be accustomed to environmental conditions, for this the pots are taken out onto the street, gradually increasing the length of stay.
Important! A temperature below + 13 ° C is detrimental to pepper.
For the entire growth period, seedlings are limited to three top dressings.
The cycle begins after the appearance of a pair of leaves, for this a solution is prepared per 1 liter of water:
- 0.5 g of ammonium nitrate;
- 1 g potassium fertilizer;
- 3 g of superphosphate.

Planting seedlings in the soil
Before planting seedlings, it is important to evaluate the land into which the seedlings will move, it should be:
- loose;
- fertile;
- let air and water in;
- saturated with organic fertilizers.
Before sowing, the soil must be moistened. Given the principles of crop rotation, soil after cucumbers, zucchini, cabbage, carrots and onions is considered to be fertile soil for pepper. Territories in which nightshade cultivated, it is better to avoid, as the likelihood of late blight is high. The soil is prepared in advance, a year before planting, organic matter is added at a rate of 5 kg per 1 m², in the autumn - potash and phosphorus substances, after which they are deeply dug. A week before the transfer of seedlings, the soil should be decontaminated by treating it with a solution of copper sulfate (1 tsp. In a bucket of water).
The seedlings are moved to the ground to the same depth at which they were originally, without exposing the roots and not digging the root of the neck. Peppers are sensitive to low temperatures, including soil, in order to protect it from freezing, they form beds 25–50 cm high at a distance of 70 cm, and we make a gap of 40 cm between bushes. The vegetable is self-pollinated, therefore it is important to sow different varieties as far away from each other friend, avoiding mixing their productive qualities.Rules for care after planting in the soil
The period after planting is quite responsible, because in order for the plant to take root and fully realize its productive qualities, it is necessary to create all the necessary conditions.
Watering
For this vegetable, moderate regular watering is recommended, the need for this is determined based on the state of the upper layer of the earth: if it has dried up, you can carry out the procedure.
Fertilizer application
Plants planted in the ground are fertilized 3-4 times with a solution of chicken droppings in a concentration of 1 part of fertilizers to 10 parts of water. Alternating it with mineral fertilizers.
The lack of nutrients is signaled by the appearance of the plant:
- the leaf is curled and a dried border appears - a lack of potassium;
- matte foliage with a grayish tint indicates a nitrogen deficiency;
- the plant says about the need for phosphorus by changing the color of the lower part of the leaf, it turns purple.
Hilling and loosening the soil
You should not miss this moment, because thanks to this, the soil is saturated with air and perfectly passes water. Hilling should be done carefully so as not to damage the root system of the plant. For this purpose, the earth is raked to the base. During hilling, weed should be removed.
Four stages of the procedure are distinguished:
- after the second watering, after 2 days, the soil is buried to a height of 6-8 cm;
- during flowering - by 10-12 cm;
- the beginning of the formation of ovaries - 14–16 cm;
- peak fruiting - 6-8 cm
As for row spacing, they are loosened, 5 repetitions are enough for a season, adhering to a number of rules:
- before flowering, loosen to a depth of 12 cm;
- during the formation of ovaries - up to 15 cm;
- at the peak of fruiting - up to 25 cm.

Basic rules for forming a bush
The formation of the bush allows you to increase the yield and size of the fetus. During the growth period, weak side shoots should be removed, and long ones should be shortened, getting rid of shaded areas. Mandatory is the disposal of all processes growing below the main fork. Such manipulations are carried out every 10 days, as well as after each harvest.
Video: How to shape pepper
Pest and Disease Control
The main diseases of pepper include:
- late blight;
- white and vertex rot;
- black leg;
- macrosporiosis.
- slugs;
- whitefly;
- scoop;
- aphid;
- a bear.

Harvesting and storage
Fruits are considered biologically ripe already on the 85th day of growth, after 30 days the technical ripeness of the culture begins. The best period for harvesting is considered an intermediate period during which the fruits contain the maximum amount of nutrients.
The first harvest occurs in early August and lasts until the first frosts. For better preservation, the vegetable is cut out with the leg. Delayed fruit harvesting leads to a halt in the formation of the following. So, regular collection makes it possible to get up to 5 generations of the crop.
Pepper is rather exacting to storage conditions and lies very little. For these purposes, undamaged fruits are taken, a part of the stem is cut off and placed in places with temperatures at the level of +8 ... + 10 ° С. For longer storage, each vegetable is wrapped with paper. They also use plastic bags that do not allow air to pass through, and the products are stored in carbon dioxide, which extends the shelf life.
When planning a pepper planting, pay attention to Fat Man, who is known for its high nutritional properties and productivity. Above are all the necessary parameters of the agricultural technology of the variety, which allows to fully realize its productivity. Follow these guidelines and grow large and tasty fruits in your yard.Did you know? Pepper ripeness is determined by the specific cod during touch.