White cabbage is one of the most popular vegetable plants. It began to be cultivated over 4 thousand years ago. Since then, breeders have bred many varieties ripening at different times, which can be cultivated in various climatic zones. The intricacies of cultivating the Stone Head variety will be discussed in this material.
Description and characteristic
 Cabbage Grade Stone Head bred in Poland. In 2006 he was added to the State Register of the Russian Federation. It is suitable for cultivation in regions where hot and dry summers are observed.
Cabbage Grade Stone Head bred in Poland. In 2006 he was added to the State Register of the Russian Federation. It is suitable for cultivation in regions where hot and dry summers are observed.
It can be grown on a large commercial scale. The stone head belongs to the late varieties - the heads ripen in 110–125 days from the moment the seedlings were planted, and in 140–165 days when grown by seedlings.
This means that they have excellent shelf life and can be stored fresh for a long time. Harvesting occurs at the end of September - October. The fruits are formed rounded, slightly flattened, dense.
Their upper leaves are painted in light green. The mass of one fetus is 3.5–4 kg. Under ideal conditions, 6 kg heads are found. The average diameter of one piece is 65–80 cm. They have excellent taste characteristics, primarily due to the high sugar level. On a 5-point scale, the taste is rated at 4.5–5 points.
The variety is characterized by high productivity - 8-10 kg / m², when grown on an industrial scale - 850–900 kg / ha, and frost resistance.
Did you know? The largest cabbage was grown by U.S. resident Scott Robb in 2012. She weighed 63 kg.
Pros and Cons of Cabbage Grade Stone Head
- The advantages of the variety include:
- high productivity;
- excellent taste of the fruit;
- frost resistance;
- ability to withstand drought;
- good keeping quality;
- Preservation of presentation in transit;
- a large mass of heads of cabbage;
- resistance to major diseases and parasites of cabbage, as well as to cracking;
- universality of application.
Among the shortcomings noted harshness of the leaves, which, however, is inherent in all fruits ripening in the late stages.

Optimal growing time
The described variety can be grown using seedlings or planted directly on an open bed. The optimal time for sowing seedlings is from April 10. Strong sprouts are transferred to open beds at the end of May.
The optimal time for planting seeds in unprotected soil without preliminary seedling cultivation is April 20–25. This method is only suitable for southern regions with a warm climate. Cultivation is carried out under a film.
Did you know? After heat treatment in white cabbage, an increase in the amount of ascorbic acid occurs. The fact is that ascorbigen, which is part of the vegetable, when heated turns into ascorbic acid.
The rules for growing varieties
In order to get healthy plants and a good harvest, you need to grow healthy, powerful seedlings. Seedling method allows you to protect plants from frost and achieve good germination of seeds. The process of growing sprouts consists of preparing seeds, soil substrate, beds in the open and replanting them in the optimal time.
Seed preparation
Seeds that are collected personally or purchased from the hands must be sorted and processed in order to prevent infection with fungal diseases. For sowing seeds of at least 1.5 mm in size are selected.

Then they are put into warm water for 15–20 minutes, heated to + 40 ... + 50 ° С, after which they are dipped in cold water for a couple of minutes. After complete drying, the seed material is treated with a fungicide, for example, Fitosporin-M or a mixture of Alirina-B with Gamair (1 tablet / 1 l of water). Duration of soaking is from 8 to 18 hours.
If the seeds are bought in a specialized store, then there is no need to select and process them against fungal infections. Soaking in warm and cold water is optional; this procedure speeds up the germination of seed material.
Growing seedlings
To plant the seeds, you must prepare the soil substrate. It can be bought in a specialized store (on the packaging it is marked “For growing seedlings”) or made with your own hands. The simplest method is mixing peat and sand in equal parts.
You can also mix the following components:
- peat, turf land, sand (75/20/5%);
- humus, sod land, sand (45/50/5%);
- turf land, humus, compost, peat (in equal parts), sand (5%).
The placement of seeds in the substrate must be carried out as follows:
- Pour and level a 3-4-cm layer of soil into a container for seedlings.
- Pour it with solutions of "Alerina-B" and "Gamair" (2 tablets / 10 l of water).
- To sustain the soil 1-3 days.
- Prepare furrows 1 cm deep. The distance between them should be 3 cm.
- Place the seeds in the furrows, observing a distance of 1-1.5 cm between them.
- Sprinkle seeds with soil substrate.
- Place crops in temperature mode + 18 ... + 20 ° С.
After this, you need to wait until the sprouts rise. This usually occurs after 4–5 days. When young plants appear, the temperature should be reduced to + 7 ... + 9 ° С. When a week passes after the seedlings have pecked, they are planted in separate pots with a diameter of 6–8 cm.  To pick sprouts, take the same substrate into which the seedlings were planted, and add double superphosphate (1 tbsp. / 1 bucket of the mixture) and wood ash (2 tbsp.) To it. Soil designed specifically for the cultivation of cabbage is also suitable.
To pick sprouts, take the same substrate into which the seedlings were planted, and add double superphosphate (1 tbsp. / 1 bucket of the mixture) and wood ash (2 tbsp.) To it. Soil designed specifically for the cultivation of cabbage is also suitable.
Picked sprouts put for 2-3 days in temperature + 17 ... + 18 ° C. To protect them from the black legs, a thin layer of river sand is poured on top of the soil. After the sprouts take root in new conditions, it is necessary to set the temperature at + 13 ... + 14 ° C during the day and + 10 ... + 12 ° C at night. Lighting should be good. In cloudy weather, additional artificial lighting is required.
Feeding is carried out when 2 leaves are formed on each plant. Use complete fertilizer containing trace elements. 12-14 days before the planned landing at a permanent place, you need to start the procedure of hardening seedlings. They take it out for a while to fresh air, gradually increasing the duration of quenching. At the same time, you can make a second top dressing from a solution of urea (1 tablespoon), potassium sulfate (1 tablespoon), water (10 liters).
Land preparation on the site
A well-lit area should be reserved for growing cabbage. The best soil for planting this vegetable plant is loam with a neutral pH level. Soil preparation should be done in the fall. Organic soil: humus, manure, compost (1 bucket / m²) are added to the well-digged area for digging.

In the spring, mineral supplements will be needed: urea (1 tbsp.), Superphosphate (1 tbsp.), Wood ash (1 tbsp.) If fertilizers were not applied in the fall, then humus is applied to each hole in early spring (0, 5 kg), nitroammophosk (1 tsp), wood ash (1/2 tbsp.)
Important! Cabbage is recommended to be cultivated on a site where carrots, potatoes, onions, legumes and grains, garlic, and cucumbers previously grew. The worst predecessors are representatives of the Cabbage family, tomatoes, radishes, turnips, beets.
Transplanting seedlings into the ground
By the time of planting, the sprouts should look strong, healthy, have a stem height of about 15 cm and 5 leaves. They need to be transplanted by transshipment, that is, without destroying the earthen coma. Wells are prepared a little larger than the root system of seedlings.

Planting depth - to the bottom leaves. Seedlings are planted without fail in the absence of sun. The distance between plants should be 45–50 cm, between rows - 50–55 cm. Immediately after planting, young sprouts need to be pruned from sunlight with agrofibre.
Important! Do not cultivate cabbage in the same place for longer than 2 years in a row. This will lead to lower yields and increase the risk of contracting diseases and harmful insects.
Basic rules for plant care
Cabbage does not require special care. It requires standard procedures: watering, loosening, fertilizing, weeding, preventive spraying against diseases and harmful insects.
Watering
Watering the newly planted seedlings is carried out 3-4 times in 7 days, 2-3 liters for one plant. After it has grown stronger and adapted to new conditions, approximately after 25-30 days, watering should be made more rare and plentiful - once every 7 days for 10-12 l / m².

For watering a vegetable plant, it is best to install a drip system. You can also produce wetting by sprinkling and furrows.
Water should be taken at a warm temperature - not lower than + 18 ° C, otherwise the risk of developing fungal infections increases significantly.
Top dressing
For cabbage, you need to spend 3-4 dressings per season. The first is carried out 14 days after the seedlings are moved to an open garden bed. At this time, it is useful to feed the plants with nitrogen fertilizers. Ready-made solutions are chosen, for example, Agricola, Sudarushka, Effekton or ammonium nitrate (10 g / 10 l of water).
The second top dressing is planned 10 days after the first. At this time, you will need to mix ammonium nitrate (1 part), superphosphate (2 parts), potassium chloride (1 part). For 1 m², you need to make 40-60 g of the mixture. During the third fertilizer application, mixtures with potassium and phosphorus are selected as the main substances. In August, cabbage is fed with fertilizers such as Autumn, nitrofoska, diammofoska.
Soil loosening
As with any vegetable plant, cultivation is very important for cabbage. They should be carried out one day after wetting or precipitation. The recommended depth of cultivation is 7 cm. This procedure avoids the formation of a hard crust on the surface of the earth and improves the flow of water, air and nutrients to the roots.

In addition to loosening, hilling will also be required. They are necessary to provoke the growth of lateral roots and improve the development of the plant. They are produced 2 times: the first time 20 days after moving to the ground, the second - 10-12 days after the first. To the stalk you need to fill the hill with earth.
Weeding
Weed removal must be done regularly. Weeds should not be allowed to obscure the cabbage and become carriers of parasitic insects. The procedure is carried out very carefully so as not to damage the root system of the plant.
Pest and Disease Control
If the agricultural technology of cabbage is done correctly, then you can count on the successful receipt of a rich harvest that is not damaged by diseases and pests. For errors made during landing and during departure, in adverse weather conditions, a vegetable plant may be affected by the following diseases:
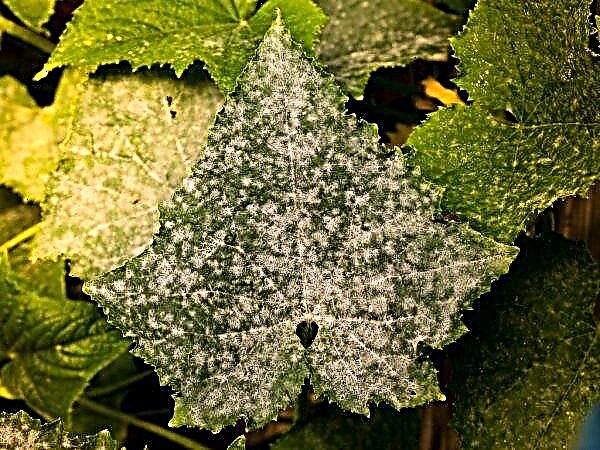
- Powdery mildew. The main symptom of the disease is the coating of leaves with powdery white coating. At the first signs of the disease, you need to remove the damaged leaves, and treat the plants with Bordeaux fluid.

- Blackleg. Manifested by darkening of the lower part of the stem. It will be necessary to get rid of diseased plants - they cannot be cured.

Of the pests for cabbage, the aphids and slugs are most dangerous. To scare away cabbage beds of pests, in the immediate vicinity should be planted beans, lettuce, celery, beans, dill, leek. Also, scattering in the aisles of wood ash also helps.
Harvesting and storage rules
Cabbage is removed when the air temperature becomes + 5 ... + 7 ° С, in dry weather. Heads of cabbage should be cut with a sharp knife, leaving a stalk about 8-12 cm high. The fruits of the Stone Head can be stored fresh until spring, without losing their juiciness. This can be achieved if you place the vegetable in an optimal microclimate.
Did you know? Sour cabbage was first used by the inhabitants of China - they soaked it in rice wine. In the 3rd century BC e. this dish was given to builders working on the construction of the Great Wall of China.
Keep the cabbage in cold conditions:
- in fridge;
- in the cellar, basement.

This variety of vegetables can be used in cooking for various purposes. Leaves of heads of cabbage can be consumed fresh in salads. They are suitable for cooking, stewing, pickling, pickling, pickling. So, Kamennaya Kamen cabbage has a number of positive characteristics, thanks to which it can be grown both in summer cottages and on an industrial scale. Her head of cabbage has a great taste, they are stored for a long time and can be used with universal purposes in cooking.