Barley storage is a volumetric technological process, which includes a number of measures. It is very important to create conditions in which the cereal will retain all its quality indicators over a long period. Storage methods may differ from each other, but be that as it may, it is important to preserve the moisture of the grain as much as possible, since this yield will determine the future yield, as well as the taste of the malt used in the production of beer.
What should be the humidity of barley during storage
The movement of moisture inside barley during storage often causes damage to the grain. Sometimes it happens that the cereal was laid in a warehouse in almost perfect condition, but separate areas with a more moistened cereal were formed. In this case, the crop may also suffer completely. This is explained by the fact that temperature changes can cause airflows that will carry moisture from one place to another. As a result, the grain begins to deteriorate everywhere.

To avoid this, It is important to control not only the barley moisture level when laying for storage, but also the temperature. Her indicator should not exceed the norm + 10 ° C. Grains are better stored at a temperature of + 9 ... + 10 ° С and humidity of 12–13% - so barley can be stored for years. If the indicator of the thermometer drops to + 5 ° C, and the humidity rises to 20%, barley will lie in the normal state for no more than 3 months.
The maximum allowable humidity of ordinary barley should be 14% during storage for up to 6 months, and 13% for longer. Great demands are placed on cereals used for brewing purposes. Its humidity should be 8% and 7%, respectively. The critical moisture value for barley is 15%. With this indicator and above, microorganisms begin to actively develop, the grain begins to “breathe”. This leads to the fact that heat is released, and the mass of the cereal and its quality decreases.
Important! Before sending grain to the store, it must be cleaned of impurities (weed grass, lumps of soil), since they can significantly raise the level of humidity.
Ambient temperature and humidity
In addition to grain requirements, there are certain conditions for the storage itself and the environment. First of all, you should consider what methods store the crop.
For this, the following conditions are created:
- specialized current platforms. Here the grain stays from the moment of harvesting until sending it for permanent storage. This does not last long, since in conditions of insecurity it is impossible to maintain the required temperature and humidity of the crop. However, plots should at least be equipped so that barley is not exposed to the negative effects of winds and rainfall. While the grain is at the site, it is cleaned and prepared for transportation to the store;
- barns. This is a kind of floor storage with a powerful ventilation system. The room must be dry and clean when laying the crop. In such warehouses, grain is distributed with a calculation of not more than 400 kg per 1 m². If the amount of barley per 1 m² is significantly greater, the humidity in the lower layers will increase, and then crop loss cannot be avoided;
- silos. These storage systems are designed for huge quantities of grain. The silo is a large stationary tower up to 30 m high. Here the grain storage process is mechanized: there is equipment for loading, unloading, moving and other special equipment. Typically, silos are placed in a group called an elevator. The warehouse automatically turns into a production and storage complex, where grain can be saved for several years with minimal losses;
- in containers. In this case, bags of coarse fabric are used as packaging, where the grain will not consume oxygen and lose its germination rate. In this way, a small batch of an elite variety, especially valuable seeds, can be stored for a short time.
 Summing up, it can be noted that the best option for storing cereals, including barley, rye, wheat and other crops, is an elevator or, in extreme cases, a barn. In storage it is necessary to ensure proper temperature conditions.
Summing up, it can be noted that the best option for storing cereals, including barley, rye, wheat and other crops, is an elevator or, in extreme cases, a barn. In storage it is necessary to ensure proper temperature conditions.
In order for barley to maintain its qualitative characteristics, the thermometer in the room should stay at + 4 ... + 6 ° С, while the optimal indicator of humidity is 60–75%. In such cool conditions, almost all biological processes cease in the grain.
This can be achieved through ventilation. It is turned on first in the fall, when the grain has the highest temperature after hot drying. In the spring, the next necessary ventilation is carried out, which will raise degrees indoors.
Important! Before stacking the grain, the store must be sanitized and disinfected using a wet or gas method.
Storage time
Barley is stored mainly in silos, but in old enterprises the barn method of saving can also be used. As mentioned earlier, the shelf life directly depends on the conditions, namely the temperature and humidity of the grain.
These indicators need to be constantly monitored, since at different times of the year they can change in one direction or another, depending on the environment. For example, by measuring the temperature of grain in different corners of the store, you can determine the areas where there is high humidity, etc.
 At a higher humidity indicator - over 30%, grain cannot be stored. It must dry properly, otherwise you can lose the whole crop.
At a higher humidity indicator - over 30%, grain cannot be stored. It must dry properly, otherwise you can lose the whole crop.
The following table presents the most accurate indicators of the shelf life of barley under certain conditions:
| Temperature | Humidity% | Shelf life |
| 9–12 ° C | 12–15 | Long time |
| 8–10 ° C | 15–17 | Up to 1.5 years |
| 5–7 ° C | 17-18 | 4-6 months |
| 18–22 | 2–4 months | |
| 22-25 | 1-2 weeks | |
| 4–5 ° C | 25–30 | 2-3 days |
Barley Drying Rules
To barley safely stored for a long time, it is dried. The process is carried out in special dryers using hot air or in vacuum plants. It is necessary to ensure that the barley moisture index is about 10%. In shaft-type plants that work with heated air, barley is fed into the upper compartment, from where it descends.
Did you know? Barley contains high-grade protein, for which he received great demand in vegetarian cooking.
At this time, heated air drying the grain is fed through the horizontal blinds. The temperature of the air masses largely depends on the humidity of the original barley: the lower its value, the more warmed up should be the air supplied by the furnace.
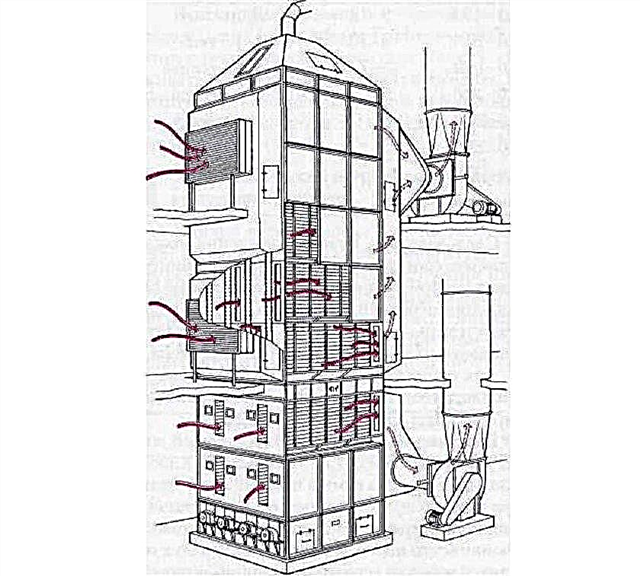 Counterflow shaft dryer for barley.
Counterflow shaft dryer for barley.
You can track the indicators using the table provided below:
| Humidity% | Heat carrier temperature, ° С |
| 16 | 95–100 |
| 19 | 85–90 |
| 22 | 78–82 |
| 24 | 70–75 |
Once below, the grain is blown with cold air and cooled. Good results are shown by the Sulzer Escher-Wyss Granifngor cooler. In the process of its work, air is supplied from below, due to which the base of the embankment is cooled, and then the upper layers.
The consequences of non-compliance with the rules
If you neglect the rules of drying and storage of barley, you can lose a significant part of the crop. Under-grain, as well as poor ventilation system lead to the formation of a crust on the surface of the embankment. Grains stick together and freeze, moldy. Most often, this phenomenon can be observed in late autumn, when the ambient temperature drops.
If you pay attention to this problem at an early stage, the crop can be saved. To do this, the “affected” seeds are mixed with dry portions in order to destroy the crust. Or, more reliably, the damaged fragments are removed. In any case, you must urgently turn on the ventilation.
 It is also necessary to regularly measure the temperature inside the grain embankment at a depth of about 0.5 m.
It is also necessary to regularly measure the temperature inside the grain embankment at a depth of about 0.5 m.
If a temperature increase of at least 2-3 degrees is noticeable, ventilation cooling must be turned on. One of the easiest ways to detect hot spots in the grain is to use a thermal rod. The device is introduced into the grain mass for several minutes, after which the data is taken out and read. Being in conditions of elevated temperature and humidity, various microorganisms, harmful bacteria are activated, because of which the crop quickly deteriorates.
Did you know? ANDFrom barley, pearl barley is made by peeling and grinding the core.
Is it possible to store barley mixed with wheat
For the production of feed grain, grain mixtures are often sown. Their main share is barley, to which wheat, rye, and oats are added. The joint planting of different crops is characterized by very weak weediness, a lesser degree of lodging of grain, which reduces yield losses. As a result, it is possible to obtain grain fodder with high nutritional qualities.
 For example, a mixture of wheat, barley and oats contains 10–15% more protein and 15–20% more fat than in single-species crops.
For example, a mixture of wheat, barley and oats contains 10–15% more protein and 15–20% more fat than in single-species crops.
During harvesting, the grain mixture is also cleaned from clogging, drying and sent for storage. It is worth noting that the wheat requirements for wheat practically do not differ from those established for barley, so crops can be stored in a mixed state.
Storage of barley should be carried out with the exact observance of technology. A negligent attitude to high-quality pre-treatment, as well as compliance with storage conditions, can lead to spoilage and huge crop losses.